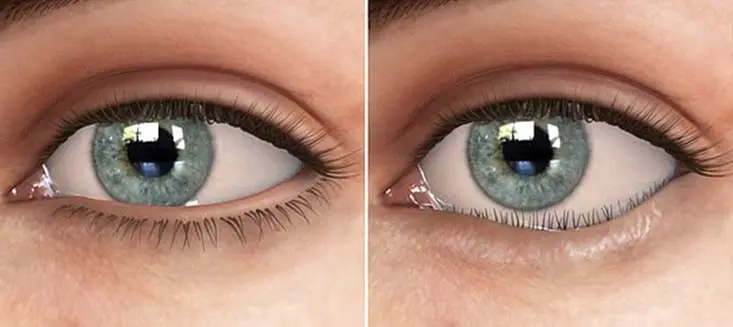
Entropion is an eye condition in which the eyelid — most commonly the lower lid — turns inward. As a result, the eyelashes and skin rub against the surface of the eye, causing irritation, a sensation of something in the eye, and in the long term, damage to the eye surface. Entropion is most frequently seen in older adults, but it can also occur congenitally, as a result of infections, or following trauma.
What Are the Symptoms of Entropion?
-
Feeling of discomfort or something in the eye
-
Redness and tearing
-
Difficulty opening and closing the eyelid
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Chronic irritation or infection of the eye surface
-
Blurred vision (in advanced cases)
What Causes Entropion?
-
Aging: The most common cause is weakening of the muscles supporting the lower eyelid.
-
Congenital structural abnormalities
-
Infections or inflammation: Especially chronic eye infections such as trachoma
-
Injuries or burns to the eyelid
-
Scar tissue formation after eye surgery
How Is Entropion Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made through a physical examination by an eye specialist. The doctor assesses eyelid movement, position, and any damage to the eye surface. If needed, tear production and corneal condition may also be evaluated.
What Are the Treatment Options for Entropion?
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the entropion.
Temporary Treatments:
-
Eye drops and ointments to protect the eye surface
-
Using tape or an eye bandage to temporarily support the eyelid outward
-
Temporary outward sutures (especially while waiting for surgery)
Permanent Treatment:
-
Surgical intervention is the most effective and permanent solution
-
The surgery involves correcting eyelid looseness, excess skin, or scar tissue
-
It is usually performed under local anesthesia and has a short recovery time
What Are the Risks of Untreated Entropion?
-
Corneal ulcers
-
Permanent vision loss
-
Chronic eye discomfort due to continuous irritation
-
Cosmetic concerns and reduced quality of life
Don't Neglect Your Eye Health
Entropion is a condition that can cause permanent damage to the surface of the eye but can be easily managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. If you are experiencing a sensation of something in your eye, redness, or irritation, consult an eye doctor without delay.